What are uterine fibroids?
In women’s uteruses, sometimes an abnormal growth occurs known as fibroids, which are also referred to as tumors that develop with fibrous connective tissue and muscle cells. The tumors’ size sometimes grows large, thereby causing severe abdominal pain and heavy bleeding during the menstrual cycle. It is quite tough to identify fibroids, as they are asymptomatic. However, it is non-cancerous.
As per the research, almost 80% of women tend to have fibroid growth, which is different in rate. Treatments are available that can help you to get relief. Fibroids are also named uterine myomas, leiomyomas, fibromas, and myomas.
Everything You Need to Know About Uterine Fibroids
Essential facts about Fibroids:
By now, we all are aware of fibroids. But, still, there are specific vital facts that you need to know. Such as,
- Fibroids are non-cancerous tissue masses, developed generally inside the uterus wall or surface.
- The size of fibroids differs. Sometimes they are like seeds and sometimes like the size of a watermelon.
- At times, a fibroid gives several symptoms and sometimes none. Some of the common symptoms include painful intercourse, pain in the pelvic area, etc.
There is a specific risk factor present while developing fibroids in the uterus and pelvis. The risk factors include,
- The risk of getting obese or overweight becomes much higher.
- Any woman can have fibroids at any age.
- Generally, it occurs at the age of 30 to 50 years, and it undergoes menopause.
These are the essential facts that you should know about the problem.
Who gets fibroids?
Fibroids are tumors, also known as myomas or leiomyomas. They are non-cancerous and have very little chance to develop into cancer. It is common in women during the childbearing years, and it may grow along the wall of the cavity as well as into the uterus.
Many women might have uterine fibroids sometime during their lives. More than 30% of women in the country develop fibroids at some point in their life. Mostly, the problem appears to those who have ages between 30 and 50 years.
Obese women or women who are overweight have a high tendency to develop fibroids in the uterus. Because of being overweight, the estrogen level (a female sex hormone) increases, and as a result, the chance of developing fibroids also increases.
The chances of getting fibroids are lower in women who’ve had children, especially those with more than one
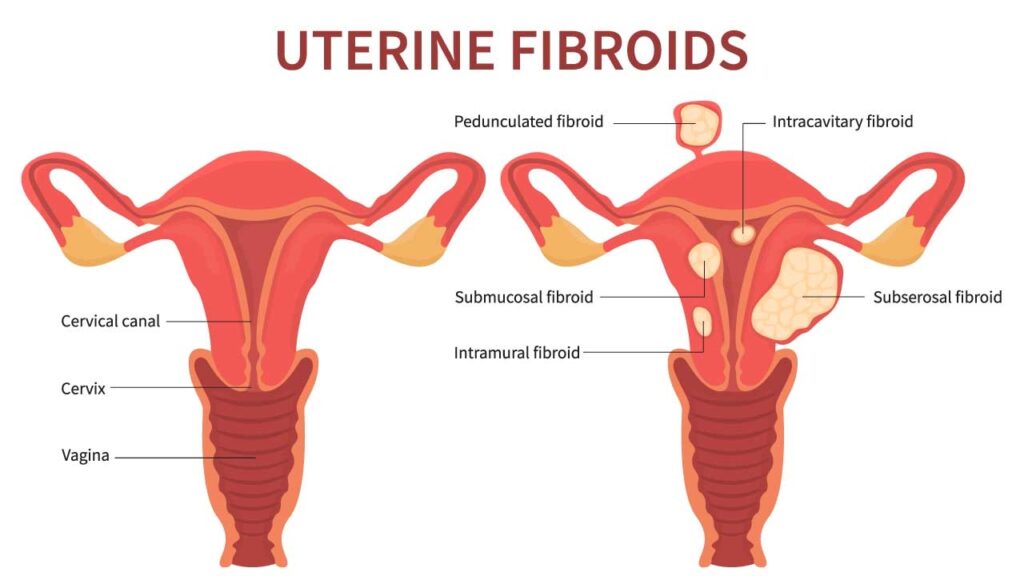
Types of Fibroids
There is a variety of fibroids, which are classified based on the location in the uterus. Hence, it is essential to know the type of fibroids. So, let us have a look below:
- Intramural fibroids
These are the most commonly occurring fibroids in women’s uteruses. You can generally notice them appearing in the uterus’s muscular cells. This fibroid tends to grow larger and more shaped, thereby stretching your womb.
- Subserosal Fibroids
It is also known as a serosa. This fibroid generally occurs in the outer part of the uterus. This also tends to grow larger, and hence the womb appears significant on one scale.
- Pedunculated Fibroids
At times, a stem is noticed by the growth of the subserosal tumor to provide support, known as a pedunculated fibroid. It generally appears like a slender base.
- Submucosal Fibroids
This is rarely formed so that you can notice. It generally appears at the middle layer of the uterus.
These are some of the essential types of fibroids that you should be aware of. Various factors lead to fibroid growth, such as hormones, any family history, or pregnancy. Hence, it would be best if you took proper measures if you do not have a fibroid. And in case you have a fibroid, you must undergo appropriate treatment so that it does not lead to something severe.
Nowadays, there are various diagnostic measures with the help of which you can quickly identify fibroids and undergo the necessary treatment that is needed.
Causes for Uterine Fibroids to Grow
It isn’t easy to find out the actual cause of forming fibroids in the uterus. Gynecologists have failed to explain why fibroids increase and shrink in size. Let’s check out some of the major factors for which the problem appears.
- Hormone Factor
The two hormones, estrogen and progesterone, stimulate the uterine lining development during each menstrual cycle in preparation for pregnancy and promote the fibroids’ growth.
- Genetic Changes
Some researchers say that fibroids could be hereditary, as many fibroids contain changes in genes that differ from those in normal uterine muscle cells. However, there is no conclusive evidence of this.
- Growth Factors
Some substances help the body maintain tissues, such as insulin-like growth factors that might affect fibroids’ growth.
- Pregnancy
You might have a question in your mind about the relationship between pregnancy and fibroids. Fibroids usually do not interfere with getting pregnant; however, it is possible that fibroids, especially submucosal fibroids, can be a reason for infertility or pregnancy loss. And some sizeable intramural fibroids that are more than 4 cm can affect fertility.
Risks of uterine fibroids during pregnancy
It may also raise the risk of certain pregnancy complications such as abruption, fetal growth restriction of the baby, preterm delivery, etc. Let’s check out the dangers of uterine fibroids during pregnancy.
- Restrict Fetal Growth:
When the fibroids’ size increases, the length of the womb decreases, and as a result, it prevents the embryo from growing.
- Placental Abruption:
When the fibroid blocks the uterine wall, the placental abruption has occurred. It may reduce the nutrients and oxygen, which are vital components of your body.
- Preterm Delivery:
When the size of the fibroids increases, you feel pain. This pain leads to uterine contractions. It leads to early delivery.
- Breach Position:
Sometimes, the baby may not be able to align for a standard delivery because of the cavity’s abnormal shape.
- Cesarean Delivery:
According to the researchers, women who have fibroids are six to seven times more likely to need a cesarean delivery than those who do not have this type of issue in their bodies.
- Miscarriage:
The chances of miscarriage are doubled in women who are suffering from this problem.
Symptoms of Fibroids
The symptoms of fibroids may vary. The symptoms of fibroids depend upon the size, location, and number of tumors. Sometimes, women don’t know they have uterine fibroids, as they cause no symptoms.
A doctor might discover uterine fibroids incidentally during a pelvic examination or prenatal ultrasound. But in symptomatic women, the most common symptoms are as follows:
- Very heavy bleeding during the menstrual cycle.
- Longer than the usual menstrual period, which is more than seven days.
- There might be a bloated feeling in the lower abdominal area.
- There would be a feeling of pressure or even pain in the pelvic region.
- A woman having fibroids may be due to constipation.
- There might be an increased urge to urinate frequently.
- You might feel pain during sex.
- Difficulty in conceiving is infertility.
- The reproductive issue includes miscarriage, preterm delivery, etc.
Here we would like to say that having any of these symptoms does not necessarily mean that you may have fibroids. These are the general symptoms and could be due to other reasons as well.
How are Fibroids Diagnosed?
Most of the time, fibroids are initially diagnosed with ultrasound. They can then be interpreted from a fertility standpoint by either a saline infusion sonogram or Hysterosalpingogram (HSG).
To confirm whether you have fibroids or not, the doctor does some necessary tests such as Hysterosalpingography, Blood test, ultrasound test, etc.
Treatment for Uterine Fibroids
- If the fibroid is well away from the cavity, it is not changing the shape of the cavity at all, and if it is not causing you any other symptoms, there is no reason you need to have it taken out.
So, doctors typically recommend that you have the fibroid taken out if it is changing the shape of the cavity or causing some of the other symptoms.
- Some doctors recommend the wait-and-watch technique to ascertain if treatment is required or not. Some suggest medications regulate your menstrual cycle or treat symptoms such as heavy menstrual bleeding and pelvic pressure. Medication will help to shrink the size of the fibroids. There are various medications available.
- Among them are gonadotropin-releasing hormone (Gn-RH) agonists. They treat fibroids by the production of estrogen and progesterone, putting you into a temporary postmenopausal state. As a result, menstruation stops, fibroids shrink, and anemia often improves in patients.
- Another essential medical treatment is a progestin-releasing IUD can relieve heavy bleeding caused by fibroids.
- One more treatment for fibroids is hysterectomy. This is the removal of the uterus and a permanent solution to prevent fibroids, which are usually indicated if the patient’s family is complete.
- Magnetic Resonance-Guided Focused Ultrasound (MRgFUS) is an advanced, non-invasive method to treat fibroids. It works by directing high-frequency ultrasound waves at the fibroid through the skin. These waves heat and break down the fibroid tissue. MRI is used during the procedure to guide the treatment and ensure it’s safe and effective, offering a quick recovery with no incisions.
- Another minimally invasive procedure is uterine artery embolization to destroy the fibroids.


